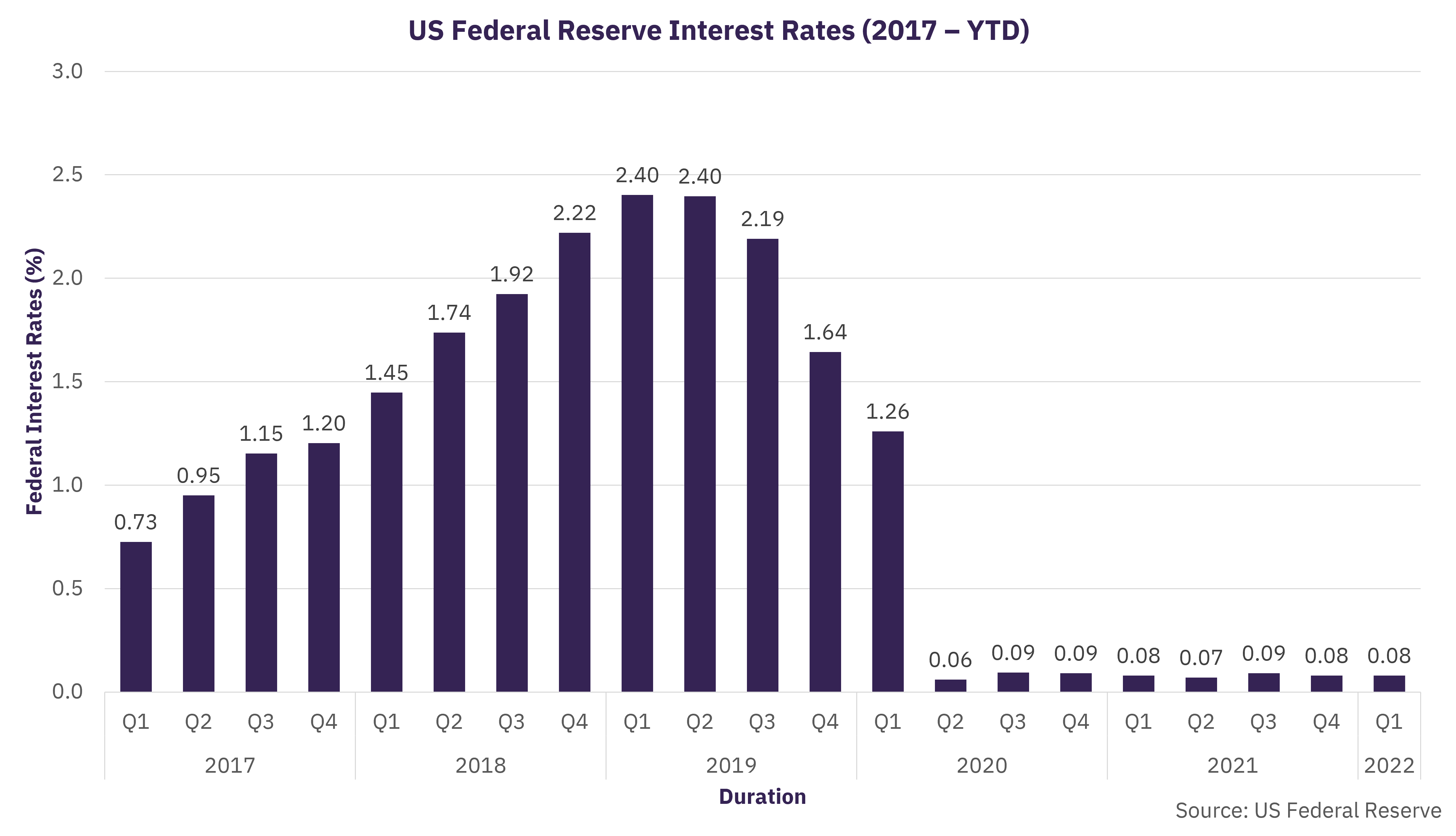
The labor market has been a key focus of attention lately, as it has shown signs of tightening. This has led to concerns that inflation could be on the rise, prompting central banks around the world to consider raising interest rates.
The Evidence of Labor Market Tightening
There is a range of evidence to suggest that the labor market is tightening. This includes:
- Strong job growth: The economy has added a significant number of jobs in recent months, and unemployment rates have fallen to historically low levels.
- Rising wages: Wages have been steadily increasing, a sign that employers are having to offer more to attract and retain workers.
- Falling labor force participation: The labor force participation rate has been declining, which means that fewer people are actively seeking work. This suggests that there is a shortage of available workers.
The Impact on Inflation and Interest Rates
The tightening labor market could have significant implications for inflation and interest rates. Here's how these two factors could be affected:
Inflation
A tightening labor market could lead to higher inflation. This is because when businesses have to pay more for labor, they often pass these costs on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Interest Rates
Central banks are likely to raise interest rates in response to rising inflation. The logic is that higher interest rates make it more expensive to borrow money, which can slow economic growth and reduce inflation. However, interest rate increases can also have negative consequences, such as slowing down investment and hurting economic growth.
Different Perspectives on Labor Market Tightening
There are different perspectives on how to interpret the tightening labor market. Some economists believe that it is a sign of a healthy economy, while others are concerned that it could lead to inflation. Here are two of the main perspectives:
Pessimistic Perspective
Economists who hold this view believe that the tightening labor market is a sign of an impending recession. They argue that the rising wages and falling labor force participation rate are evidence that the economy is nearing a peak, and that a downturn is likely to follow.
Optimistic Perspective
Economists who hold this view believe that the tightening labor market is a sign of a healthy economy. They argue that the strong job growth and rising wages are evidence that the economy is growing, and that this will continue to create opportunities for workers.
Data and Evidence on Labor Market Tightening and Inflation
To determine the overall state of the labor market and its impact on inflation, let's look at data and evidence from various research and reliable sources.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics: According to BLS data, the U.S. economy added over 528k jobs in July 2022, with the unemployment rate dropping to 3.5%. These figures indicate a robust job market, supporting the notion of labor market tightening.
- Federal Reserve Report: The Federal Reserve has noted that wage growth has accelerated in recent months. The Employment Cost Index, which measures the overall cost of labor, showed a 5.1% increase in wages and salaries for the year ending in March 2023. Rising wages suggest that employers are facing competition for skilled workers, potentially contributing to inflationary pressures.
- World Economic Forum: A study by the World Economic Forum found that a significant number of businesses are struggling to find the talent they need, with 40% of global respondents reporting challenges in recruiting skilled workers. This highlights the global nature of labor market tightness, indicating a potential shortage of available labor.
- International Monetary Fund: The IMF has cautioned that the tightening labor market could lead to higher inflation, especially in countries where there are structural rigidities in the labor market. They emphasize the need for central banks to carefully navigate the balance between supporting economic growth and containing inflationary pressures.
Conclusion: Policy Implications and Broader Impacts
The tightening labor market presents a complex dilemma for policymakers. On the one hand, it is a sign of a strong economy with low unemployment and rising wages. On the other hand, it could also lead to higher inflation and interest rates, which could slow economic growth and hurt consumers.
The key challenge for policymakers is to find a way to address the tightening labor market without causing undue harm to the economy. This will likely require a careful balancing act, with central banks gradually raising interest rates to curb inflation while also supporting economic growth.
In addition to the policy implications, the tightening labor market could also have broader impacts on the economy and society. For example, it could lead to:
- Increased labor force participation: Higher wages could encourage more people to enter the workforce, potentially increasing the size of the labor force.
- Increased investment in automation: Businesses may invest in automation to offset the rising cost of labor, which could lead to job displacement in some industries.
- Greater demand for training and education: As businesses face skills shortages, they may invest more in training and education programs to develop their workforce.
The tightening labor market is a complex and dynamic issue with significant implications for the economy and society. It will be important to monitor the situation closely and adjust policies as needed to ensure a sustainable economic recovery.
Read also:
How Many Stars Are In The Universe?
Schumer Torpedoed By Manchin And Sinema On Crucial NLRB Vote
TIME Celebrates 100 Years Of Trusted And Impactful Storytelling