Seismic Hazards in Reno: A Critical Examination
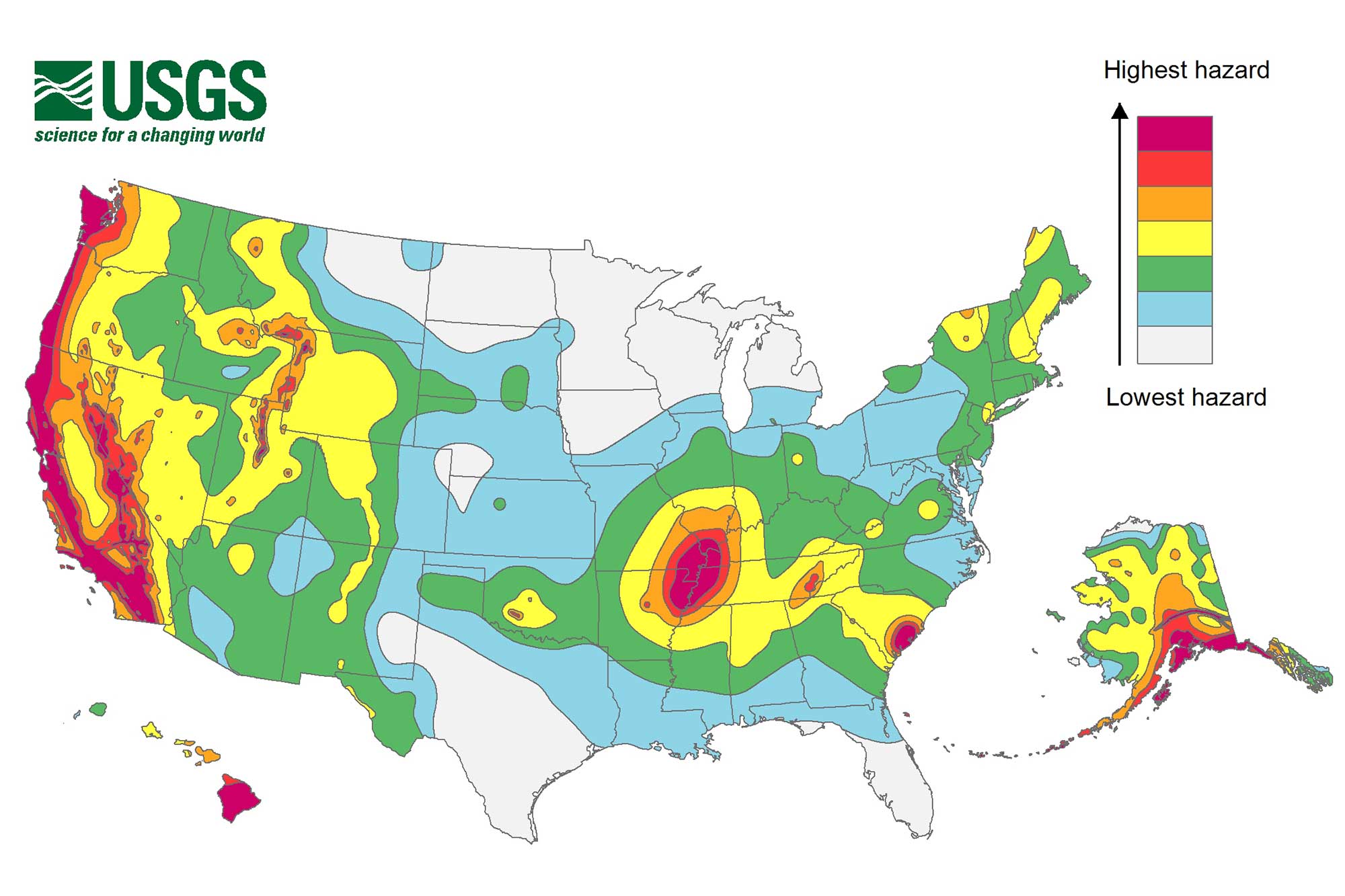
Reno, Nevada, is a city located in a seismically active region known as the Basin and Range Province. This region is characterized by numerous faults capable of producing significant earthquakes. The potential for seismic activity poses a significant hazard to Reno and its surrounding communities, and it is crucial to understand the complexities of these hazards to mitigate their impact.
Fault Lines and Seismic Activity
Reno lies near several major fault lines, including the Sierra Nevada Fault, the Walker Lane Fault, and the Humboldt Fault. These faults have a long history of seismic activity, with several significant earthquakes occurring in the region in the past century. The 1932 Cedarville earthquake, with a magnitude of 7.6, caused widespread damage and loss of life in the area.
Earthquakes occur when tectonic plates move, causing stress to build up on faults. When the stress exceeds the strength of the rock, the fault ruptures, releasing energy in the form of seismic waves. The magnitude of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale, with higher numbers indicating more powerful earthquakes.
Ground Shaking and Liquefaction
The primary seismic hazard in Reno is ground shaking, which can cause buildings to collapse, infrastructure to fail, and landslides to occur. The intensity of ground shaking varies depending on the magnitude of the earthquake, the distance from the epicenter, and the local geology.
Another significant seismic hazard in Reno is liquefaction. This occurs when loose, water-saturated soils lose their strength during an earthquake, behaving like a liquid. Liquefaction can cause buildings to sink or tilt, underground utilities to rupture, and roads to buckle.
Building Codes and Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the impact of seismic hazards, Reno has adopted stringent building codes that require new construction to meet specific seismic design standards. These codes specify the minimum requirements for building materials, structural elements, and foundations to withstand earthquake forces.
Additionally, Reno has implemented various seismic retrofitting programs to strengthen existing structures. These programs involve identifying vulnerable buildings and implementing measures to improve their seismic resistance. Retrofitting can include adding shear walls, reinforcing concrete structures, and replacing old foundations.
Public Education and Preparedness
Public education and preparedness are crucial for reducing the risks associated with seismic hazards. The Nevada Seismological Laboratory provides earthquake monitoring and outreach programs to educate the public about earthquake science and safety. Regular earthquake drills are conducted to practice emergency response procedures.
Individuals can also take steps to prepare for earthquakes by securing furniture, having an emergency kit, and developing an emergency plan. It is essential to be aware of potential evacuation routes and safe places to take shelter during an earthquake.
Conclusion
Seismic hazards pose a significant challenge to Reno and its surrounding communities. The presence of numerous fault lines, the potential for ground shaking and liquefaction, and the need for ongoing mitigation efforts highlight the importance of understanding and preparing for these hazards.
By adopting stringent building codes, implementing retrofitting programs, and engaging in public education and preparedness initiatives, Reno is taking proactive steps to minimize the impact of earthquakes. However, continued research, monitoring, and community involvement are essential to further reduce seismic risks and ensure the safety of residents.
Read also:
Bomb Cyclone Poised To Unleash Fury On Ireland And British Isles
Edwards' Dominance Propels Timberwolves Past Knicks In 116-99 Victory
Ohio State Favored Over Notre Dame In College Football Playoff National Title Game