1500 Years of Silk Road Legacy: Exploring the Ancient Routes of Trade and Culture
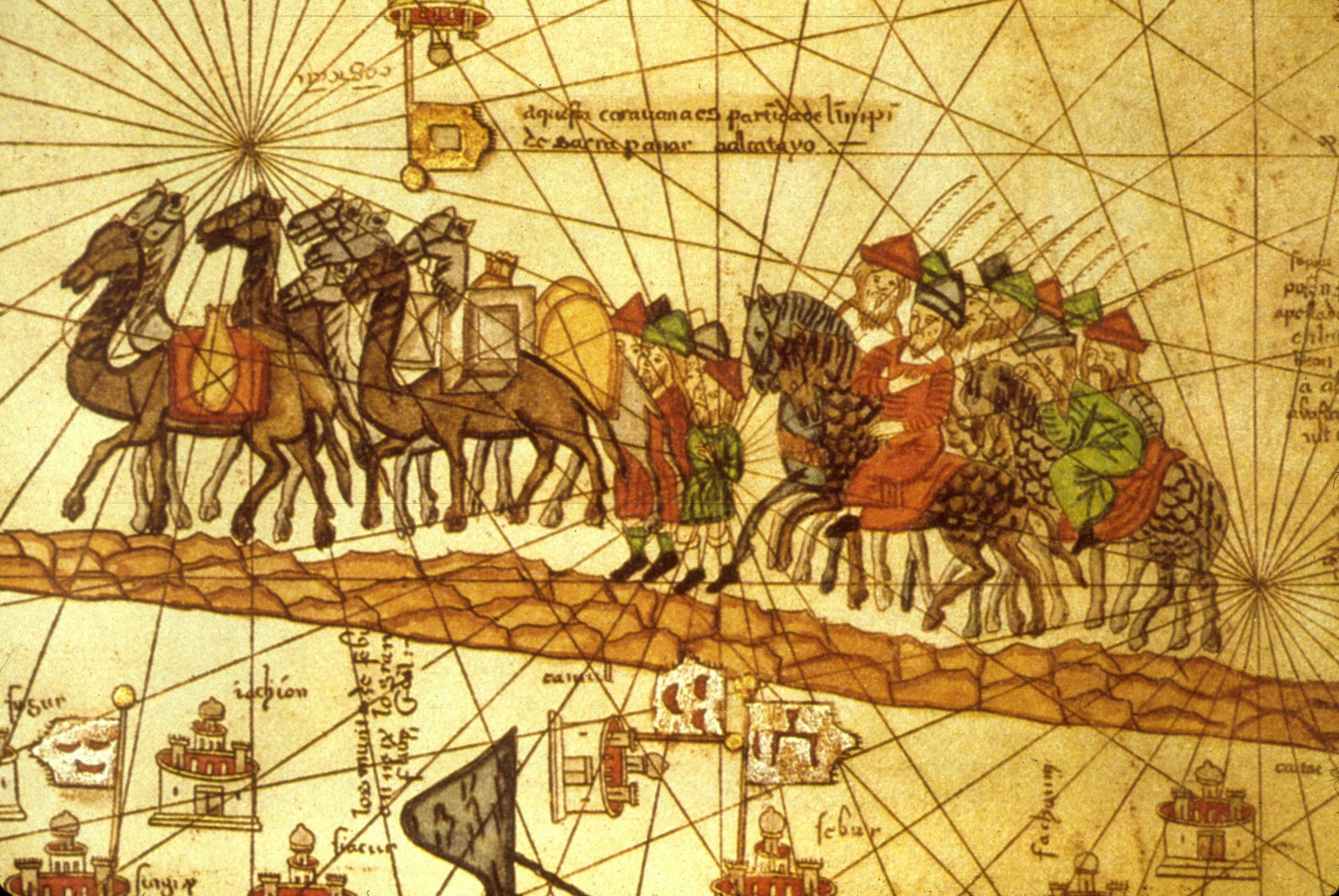
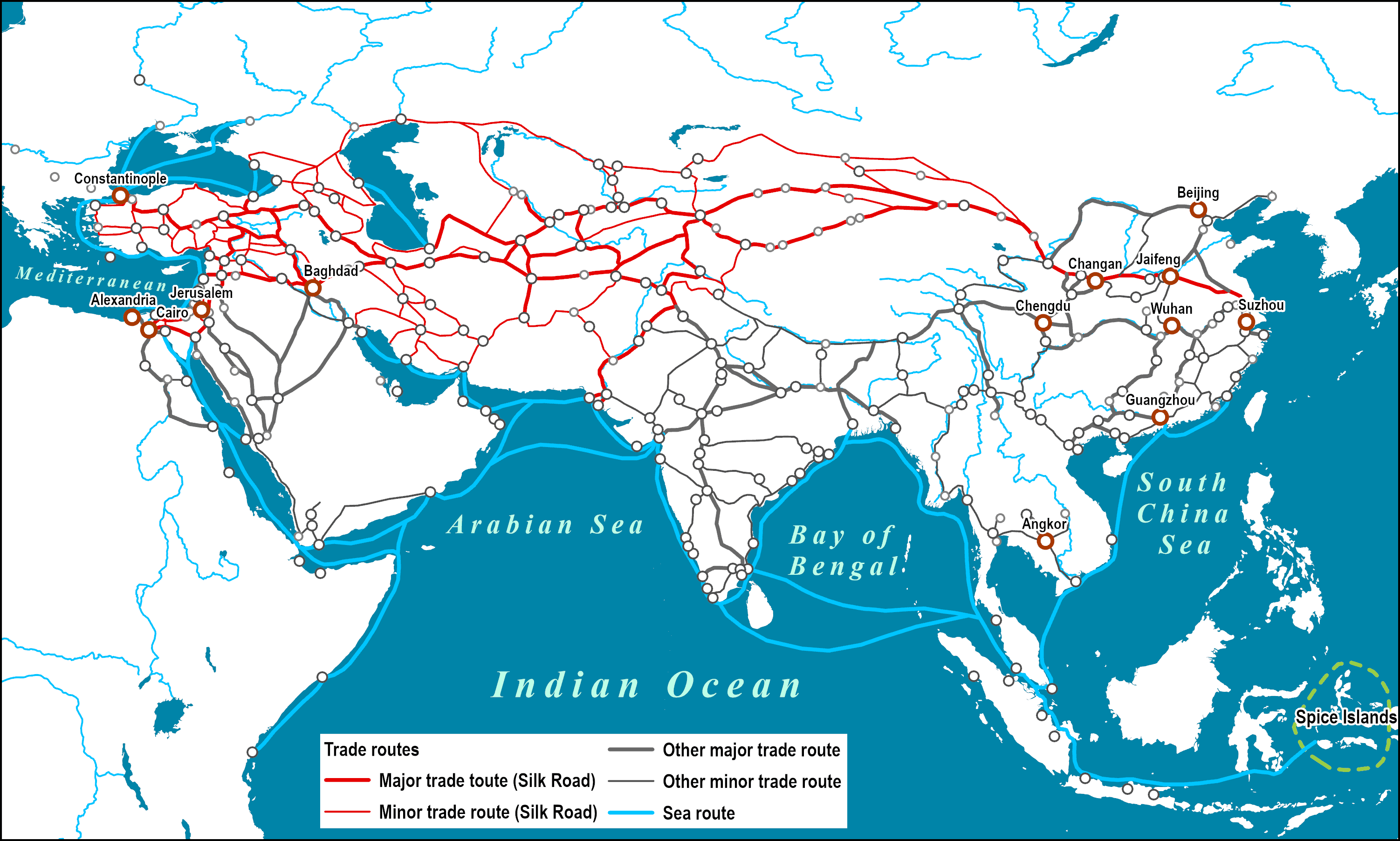
The Silk Road, a vast network of interconnected trade routes spanning thousands of kilometers, served as a conduit for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between East and West for over fifteen centuries. This legacy has left an enduring mark on civilizations across Eurasia, shaping historical trajectories, economies, and cultural identities.
The Origins and Significance of the Silk Road
The term "Silk Road" was coined by 19th-century German geographer Ferdinand von Richthofen to describe the intricate web of routes that facilitated trade between China and the Roman Empire. However, historical evidence suggests that these routes existed long before its official nomenclature. In the 2nd century BCE, the Chinese Han dynasty established diplomatic missions to Central Asia, opening up trade channels with kingdoms in the region. Over time, these routes extended westward to Persia, the Middle East, and eventually Europe.
The Silk Road was not a single, fixed path but rather a complex system of land and sea routes that adapted to shifting political, economic, and geographical conditions. It consisted of a primary northern "Silk Road" and a southern "Maritime Silk Road." The northern route passed through Central Asia, traversing the Gobi Desert and the Pamir Mountains, while the southern route connected China with Southeast Asia, India, the Arabian Peninsula, and East Africa.
The Commodities and Cultural Exchange
The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of a wide range of commodities, including silk, tea, spices, horses, gold, and silver. It served as a vital conduit for the transmission of technologies, such as papermaking from China to the West and the introduction of gunpowder in the East. Beyond material goods, the Silk Road also played a crucial role in the exchange of ideas, religions, and cultural practices. Buddhism spread from India to China along the Silk Road, while Islam later spread eastward from Persia and the Middle East.
Historical Impact on Civilizations
The Silk Road had a profound impact on the development of civilizations along its routes. Cities like Samarkand, Bukhara, and Xi'an became vibrant centers of trade and culture, attracting merchants, scholars, and travelers from afar. The exchange of goods and ideas led to the development of new languages, religions, and artistic traditions. For example, the spread of Nestorian Christianity from the Roman Empire to China via the Silk Road resulted in the creation of a unique blend of Eastern and Western religious beliefs.
Modern Revival and Legacy
In recent decades, there has been a renewed interest in the Silk Road, both as a historical phenomenon and as a potential catalyst for modern economic and cultural exchange. China's Belt and Road Initiative, launched in 2013, aims to revive and expand the ancient Silk Road through infrastructure development and economic cooperation. However, the initiative has also been criticized for its potential environmental and geopolitical implications.
The legacy of the Silk Road continues to shape global affairs today. It reminds us of the interconnected nature of human history and the transformative power of cultural exchange. By understanding the complexities of the Silk Road, we can gain insights into the challenges and opportunities of globalization in the 21st century.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its historical significance and modern revival, the Silk Road has also been the subject of controversy and debate. Some historians argue that the "Silk Road" is a Western construct that oversimplifies the complex web of trade routes and cultural interactions that existed in ancient Eurasia. Others critique the Belt and Road Initiative as a neo-colonialist project that favors Chinese economic interests.
Furthermore, the modern revival of the Silk Road raises environmental concerns. The expansion of infrastructure projects along the routes could lead to increased resource consumption, pollution, and habitat loss. Striking a balance between economic development and environmental sustainability remains a key challenge for the future of the Silk Road.
Conclusion
The 1500-year legacy of the Silk Road is a testament to the power of trade and cultural exchange to shape the course of human civilization. By facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, the Silk Road fostered the development of new societies, religions, and artistic traditions. While modern revivals of the Silk Road offer opportunities for economic cooperation, they also present challenges that must be navigated with care.
Understanding the complexities of the Silk Road is crucial not only for appreciating its historical significance but also for informing contemporary debates about globalization and the interconnectedness of the world. By examining the past, we can gain insights into the present and shape a more sustainable and equitable future.
Read also:
Trump And Newsom's Unlikely Alliance: Surprising MAGA Support For Pro-Immigration Stance
Donald Trump On FBI Director Christopher Wray
Wes Bentley Talks Challenge Of Keeping 'Yellowstone' Ending A Secret